Contents
Securing copies of the China Business License is an essential task for businesses operating within China or engaging in partnerships with Chinese companies. This step-by-step guide aims to simplify the process, providing you with clear instructions on how to obtain the original and duplicate copies of your China Business License. Perfect for both international businesses navigating the Chinese market and domestic enterprises in need of official documentation, this guide breaks down the application steps, required documents, and tips for a successful submission. Embark on this journey with us to ensure you have the necessary paperwork to support your business endeavors in China.
Defining the China Business License
The Business License is an official document mandated by laws such as the “Company Law of the People’s Republic of China,” certifying a business’s eligibility to operate legally within Mainland China. Depending on the business’s nature and scale, licenses vary across several types, including Limited Companies, Limited Liability Companies, Joint Venture Companies (JV), Representative Offices (RO), and Foreign Limited Partnerships (LP), each with distinct operational scopes and responsibilities.
Original and Duplicate Copies of the China Business License
The China Business License comprises an original and a duplicate, each holding equal legal standing. The original is safeguarded by the company for use in official and legal matters, whereas the duplicate facilitates everyday commercial activities. This system ensures the license’s security and practicality.
- Social Credit Code: This is the 18 digital unified social credit code of the company.
- Registration number: This is the official registration number of the company in SAMR.
- Official company name: This is the registered company’s name in Simplified Chinese Language according to the Company Law.
- Type of Enterprise: This is the type of corporation in which the company is incorporated. (WFOE, LLC, JV, RO, LTD, etc.)
- Legal representative: The legal representative is the only person who is entitled to sign legally binding documents for the company and is responsible for any action of the company.
- Business Scope: This is the list of business activities that the corporation will be able to carry out in China.
- Registered capital: The registered capital is divided into Pay-in capital and Subscribed capital. It has to be paid within a certain time limit (20-30 years).
- Date of establishment: This is the date the business license was issued.
- Expiry Date: This is the operation of the company’s expiry date.
- registered Address: Every company requires a real address as the registered address. Once the Lease contract expired without renewal, the company will be blacklisted in the SMAR.
- QR Code: This is the Company’s QR Code linked to the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System.
Acquiring a China Business License
Securing a Business License requires registration with the State Administration for Industry and Commerce or its regional counterparts. Applicants must submit comprehensive business plans, capital verification, and shareholder details. Foreign investors are additionally subject to specific foreign investment regulations, emphasizing the stringent process to comply with national standards.
Please read the What is the the Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) in China Business License.
English Version of the Business License
All official documents, including the China Business License, are issued in Chinese. Although China is open to foreign enterprises, there is no legal obligation to provide licenses in English due to the precedence of Chinese as the official language. Foreign entities may have the document translated and notarized for international transactions or legal uses.
Digitalization of the Business License
The digital transformation in China includes the progressive digitalization of the Business License. This advancement simplifies management, enhances efficiency, and mitigates fraud risks, allowing businesses to handle their licenses online and reflecting China’s push towards business facilitation and legal clarity.
Verifying a China Business License
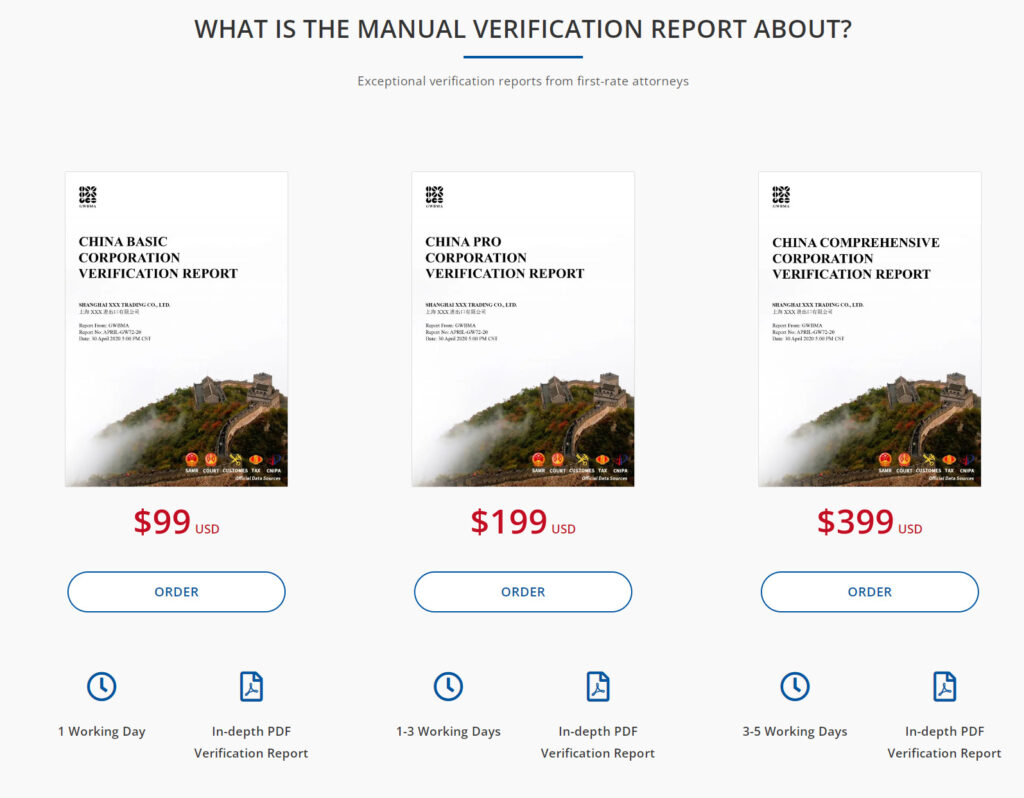
Verifying a Business License is a vital step before business transactions, containing essential information about the company’s legal standing. With technology’s evolution, two expedient verification methods are now available: the Manual Company Verification Report and the Instant Automated Company Report, both ensuring fast and accurate access to a company’s licensing information.
Significance for Foreign Enterprises
For foreign companies looking to enter the Chinese market, comprehending the Business License process is essential. Despite potential language and cultural barriers, accurate license knowledge helps mitigate legal risks and establish a valid business presence. The move towards digital licenses and improved verification processes further streamlines research and partner assessments, promoting success in the Chinese marketplace.
Conclusion
Understanding the Business License is fundamental for businesses operating or planning to enter China. By recognizing its importance, mastering the acquisition and verification procedures, and utilizing modern technology for enhanced information access, companies are better positioned to navigate this market’s opportunities and challenges. As China continues to open its doors wider, familiarity with such key commercial regulations grows increasingly crucial for global entrepreneurs and investors.
In conclusion, GWBMA is committed to assisting global entrepreneurs and investors from company registration, trademark, copyrights, patents, to legal services. By focusing on detailed and comprehensive, secure, and rapid services, GWBMA ensures you experience our dedicated support, enabling you to efficiently start your business in China.