Contents
Introduction:
In the past, Hong Kong held a higher position than Singapore among global financial centers, but the situation changed in 2022 and 2023. According to the latest 2024 Global Financial Centres Index (GFCI), Singapore again overtakes Hong Kong to become Asia’s top financial center, ranking third globally, just behind New York and London, while Hong Kong is now fourth. For decades, Hong Kong has been the leading financial center in Asia, especially during the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Hong Kong’s geographic advantage, free-market economy, strong legal system, and close ties with mainland China attracted many international financial institutions and companies. Even during the global financial crisis, Hong Kong maintained robust financial services and trade capabilities. However, in recent years, Singapore has gradually closed the gap with Hong Kong and has taken the lead in certain aspects. The Singaporean government has implemented a series of reforms and policy measures to attract many financial institutions and international companies. Why has this change occurred for the first time? This article explores the reasons behind Singapore overtaking Hong Kong as Asia’s top financial center by analyzing the differences between Singapore and Hong Kong in terms of political, economic, geopolitical, and social factors.
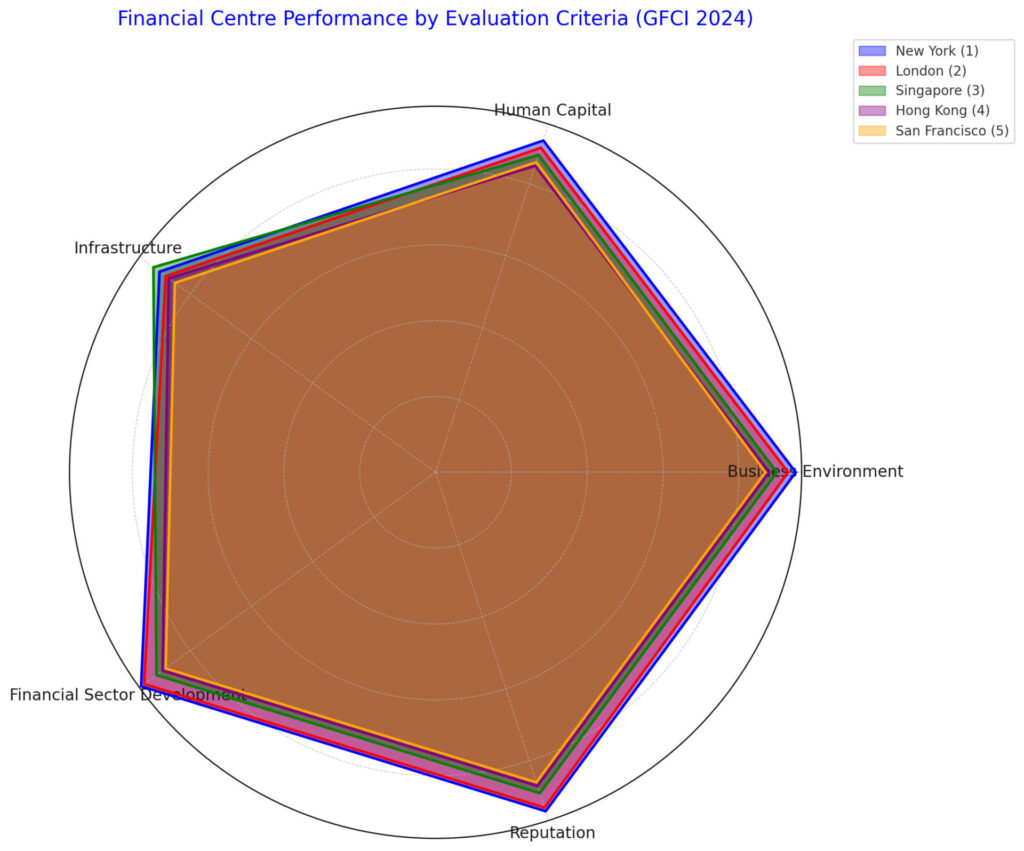
| Financial Centre | Business Environment | Human Capital | Infrastructure | Financial Sector Development | Reputation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York | 95 | 92 | 90 | 96 | 94 |
| London | 93 | 90 | 88 | 95 | 93 |
| Singapore | 90 | 88 | 92 | 91 | 89 |
| Hong Kong | 88 | 85 | 87 | 89 | 87 |
| San Francisco | 87 | 86 | 85 | 88 | 86 |
Singapore Overtakes Hong Kong: The Changing Reasons
Both Singapore and Hong Kong face the challenges and opportunities brought by globalization and technological change. They need to continuously adapt to changes in the global economic environment, promote innovation and technological progress, and maintain their competitiveness in international finance and business.
Both have engaged in fierce competition to attract international financial institutions, multinational companies, and investment. In recent years, Singapore has gradually overtaken Hong Kong to become Asia’s largest financial center, mainly due to Singapore’s stable political environment, strict financial regulatory system, favorable tax policies, and open economic policies. In contrast, Hong Kong has been affected by political turmoil and strict epidemic prevention measures. As geopolitical tensions between China and Western countries intensify, Hong Kong, as part of China, has seen its international status and attractiveness impacted. Consequently, some international companies and financial institutions have chosen to set up regional headquarters in Singapore to avoid potential political risks. Simultaneously, more foreign enterprises are registering companies in both Singapore and Hong Kong.
Despite the competition, Singapore and Hong Kong have extensive cooperation in the economic and trade fields. Both are free ports and international trade hubs, promoting regional economic integration through complementary economic structures and policies. Trade and investment ties between Singapore and Hong Kong are close, supporting economic development in both regions. Additionally, Singapore and Hong Kong play vital roles as important financial and business hubs in Asia, participating in regional economic cooperation mechanisms such as ASEAN and APEC, and jointly promoting regional economic development and policy coordination.
Why Singapore Overtakes Hong Kong: Unique Advantages
China’s rapid economic growth over the past decades has significantly enhanced Asia’s overall economic status. As the leading economy in Asia, China’s development has provided Singapore with more business and investment opportunities. First, the economic and trade relationship between Singapore and China is very close. Singapore is an important node in China’s Belt and Road Initiative, and the two countries have in-depth cooperation in various fields, including infrastructure, financial services, and technological innovation. Secondly, China’s vast market and economic vitality have attracted many international companies to use Singapore as a gateway to the Chinese and Asian markets, increasing Singapore’s attractiveness as a financial and business hub.
Global Changes Lead to Singapore Overtaking Hong Kong
Geopolitical tensions between Western countries and China have also affected the status of both Hong Kong and Singapore as financial centers. Especially with the United States and other Western countries imposing certain policies and sanctions on China and Hong Kong, international capital flows in Hong Kong have been impacted. This capital might choose the more neutral and stable Singapore as an alternative. Additionally, with Hong Kong’s strengthened ties with mainland China and political changes under the “One Country, Two Systems” policy, some international companies and financial institutions have adopted a wait-and-see attitude towards Hong Kong’s future. Some companies, considering risk management, might choose to relocate their regional headquarters or part of their operations to Singapore.
Singapore Overtakes Hong Kong, The Special Reasons
Another important reason is that many wealthy Chinese individuals choose to immigrate to Singapore. Singapore is one of the world’s leading wealth management centers, attracting a large number of high-net-worth individuals. According to wealth reports, a significant portion of the private wealth managed in Singapore comes from wealthy Chinese. The key point is that Singapore implements a lower progressive tax rate on personal income and has no capital gains tax or inheritance tax, which is highly attractive to high-net-worth individuals. Upon immigration, these wealthy individuals bring substantial funds into Singapore, enhancing the local wealth management level and promoting the development of the local real estate and financial markets. In practice, after immigrating to Singapore, wealthy Chinese individuals typically deposit large sums in Singaporean banks or invest in Singaporean real estate, stock markets, and other financial products. These factors collectively strengthen Singapore’s position as a global financial center. Certainly, there are many other reasons, which I will not detail individually.
Improved Phrase: Factors Behind Singapore Overtaking Hong Kong
According to 2023 statistics, Singapore has a population of about 5.8 million, with approximately 74% being Chinese, 13% Malay, and 9% Indian, with other ethnic groups making up the rest. Although English is the official language, Mandarin is also widely spoken due to the large Chinese population. Currently, Singapore has about 1.77 million foreigners, accounting for nearly 30% of the total population. These foreign residents include various types of foreign workers, families, and international students.
As of 2024, Hong Kong has a population of about 7.498 million. Hong Kong has a large number of foreign residents, including professionals and workers from around the world. Through different immigration and talent programs, Hong Kong has attracted many expatriates and families. Over the past year, Hong Kong has seen an influx of 174,000 people, including 31,000 one-way permit holders from mainland China.
First, Singapore’s stable political and economic environment is a key factor. The Singaporean government ensures the confidence of enterprises and investors with its transparent legal system and strict anti-corruption measures. In contrast, Hong Kong has experienced social unrest and political changes in recent years, negatively impacting its status as a financial center.
Secondly, Singapore’s attractiveness to talent and enterprises continues to increase. Singapore offers favorable tax policies, convenient visa systems, and high-quality education and training systems, giving Singapore an advantage in the global talent market. In contrast, Hong Kong’s strict quarantine policies during the pandemic led to a significant loss of talent.
Moreover, Singapore is highly open and internationalized. Singapore actively participates in global trade and financial networks, becoming the preferred location for many multinational companies to set up their Asian headquarters. Hong Kong’s strict pandemic prevention policies have, to some extent, restricted international exchanges and activities.
Lastly, Singapore has advanced infrastructure and a technological environment, providing solid support for fintech and innovation. Singapore’s leading position in fintech attracts a large amount of investment and enterprises, further enhancing its competitiveness as a financial center. Singapore’s international image and reputation continue to improve. By hosting large international conferences and events, Singapore increases its global visibility and influence, solidifying its position in the international financial market. These factors together have enabled Singapore to lead Hong Kong in the global financial center rankings.
Conclusion:
The relationship between Singapore and Hong Kong involves both competition and cooperation, with both playing important roles in international finance and business. Although Singapore has overtaken Hong Kong for the first time and outperformed Hong Kong in various competitiveness indicators, there remains a broad space for cooperation in regional economic integration, trade, and talent exchange. Furthermore, GWBMA and its counterparts in Singapore and Hong Kong have deep cooperation relationships to help foreign enterprises enter the Asian market across various industries.
As the global economic environment changes, both Singapore and Hong Kong need to continuously adapt and adjust to maintain their important positions on the international stage.