China’s USD 163 billion in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows last year, compared to USD 134 billion attracted by the United States, according to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) Investment Trends Monitor published on 20th January 2021.
In 2019, the United States had received USD 251 billion in FDI inflows and China received USD 140 billion. But in 2020, China received USD 163 billion in inflows last year, compared to USD 134 billion attracted by the U.S.
Foreign Direct Investment Trends Monitor in 2020
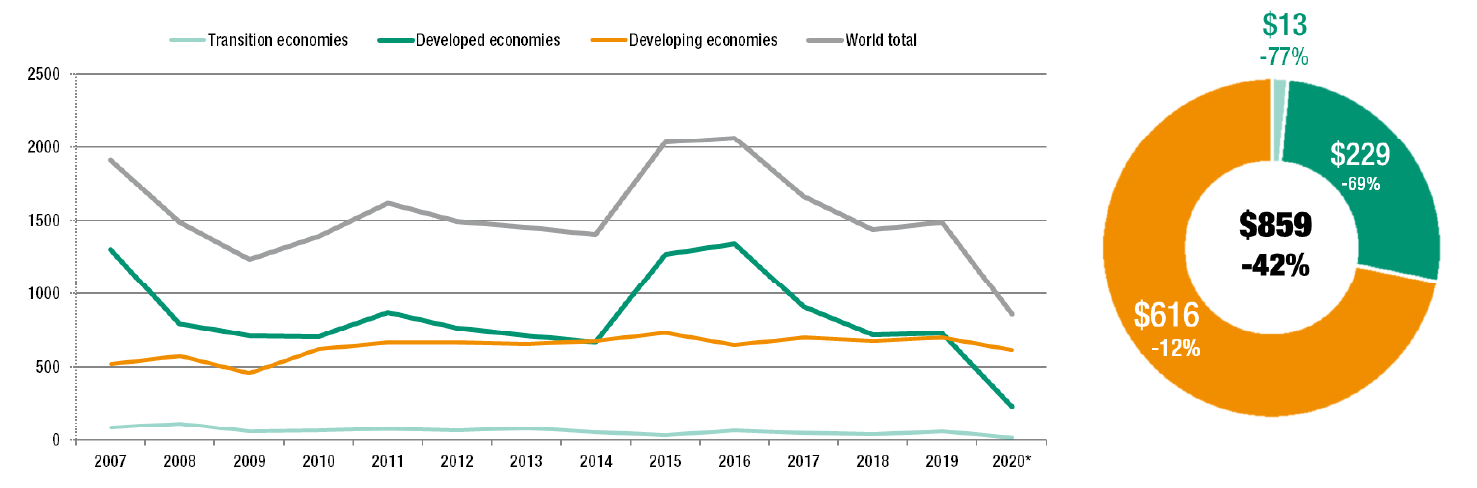
As a result of the COVID-19, the overall global flows cratered by 42%. Flows fell to an estimated USD 859 billion from USD 1.5 trillion in 2019, according to the UNCTAD Investment Trends Monitor. It was the lowest level since the 1990s and 30 % below the investment trough that followed the 2008-09 Global Financial Crisis.
As the world struggled to contain the coronavirus crisis, FDI in the United States plummeted 49% in 2020 while investment in China rose 4%, making China the largest recipient of Foreign Direct Investment for the first time.
China managed to largely get coronavirus under control within its borders last year, despite being the first nation to be hit with the deadly disease. Besides that, China’s government instituting strict, large-scale lockdown measures in early 2020.
By April 2020, 99% of Large-Scale Industrial Enterprises (LIEs) and 84% of Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) had restored their production nationwide. The rate of personnel returning to work was 94 percent by this time.
A senior official with the Chinese Commerce Ministry said many foreign companies adopted a “wait and see” attitude in the early stage of the pandemic, but they are now expanding their investments. Companies like BMW, Siemens, LG, and Toyota plan to make big investments in China.
Key projects of FDI in China
According to official data released by China’s Ministry of Commerce, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into China rose by 5.2% year-on-year to USD 107.2 billion in the first nine months of 2020, with 22,602 Foreign-Invested Enterprises (FIE) having newly established by the end of August. In September, FDI inflows into China reached USD 14.25 billion, up by 25.1 %, as compared to the same period last year. Leading Multinational Corporations (MNCs), such as ExxonMobil, BMW, Toyota, and Invista, increased their investment in China.
These key projects are mainly in the manufacturing, industry, and High-Tech sectors. The Chinese government has helped them to quickly resume operations, resolve logistic problems, and enable 10,000 high-level foreign management personnel and technicians to enter China. Meanwhile, China issued the Regulations to Encourage the Establishment of Regional Headquarters (RHQs) by Multinational Corporations (MNCs) in 2019 with special Subsidies for Encouraged Development of RHQs” to RHQs and foreign-invested R&D centers. Such subsidies contain supportive funds for company set-up and office rentals, incentives depending on the RHQs’ annual turnover, etc.
Conclusion
The Chinese Commerce Ministry said that the country managed to emerge from COVID-19 and meet its target of stabilizing foreign investment in 2020, bucking the downward trend in global foreign investment. Among Chinese sectors, high-tech industries saw an FDI increase of 11% in 2020, and cross-border mergers and acquisitions rose by 54 %, mostly in information and communications technology, and pharmaceutical industries.